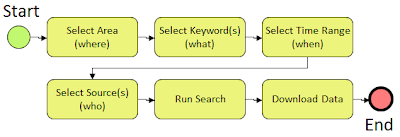
Searching for Time Series Data
When searching for data in HydroDesktop, you can specify the following filters:
- Area of interest
- Keywords (e.g., Precipitation)
- Time range
- Data sources
Once you initiate a search, HydroDesktop queries the CUAHSI-HIS national catalog of known time series data to find locations of time series that match your search. Search results are presented in the map and include information that HydroDesktop can use to connect to each individual data provider for data access.
You can then further filter the results and choose which data you want to actually download.
The tools for running a search are located on the Search tab of the HydroDesktop ribbon. The panels in this tab represent the steps in the workflow above.
Specifying Area of Interest
There are two ways of specifying an area of interest for the search: drawing a box or selecting a polygon.
Drawing a Box
If you are very familiar with the location of your study area, then drawing a box may be the easiest option.
To draw a box around your area of interest:
1. Use the tools on the Map tab to locate and zoom in to your area of interest.
2. On the Search tab, click the Draw Rectangle tool.
3. With the left mouse button, click and drag in the map to draw a box around your study area.
Once a box is drawn, it is highlighted in the map
Selecting a Polygon
If a polygon feature in the map represents your area of interest, you can select that polygon to be used in the search. For example, the polygon could represent a county as found in the U.S. Counties dataset included with HydroDesktop, or the polygon could come from a shapefile that you created and added to the map.
You can either select polygons by location or by attributes of the polygon feature.
To select polygons by location:
1. In the Legend, left-click to select the map layer that you want to use. Note that you must select a polygon layer. The search will not work with online basemap data, point layers, or line layers.
2. In the Legend, make sure the desired map layer is visible by placing a check in the box next to the layer’s name.
3. On the Search tab, click the Select Features tool. This tool works like the Select tool on the Map tab, and either tool can be used to select features.
4. With the left mouse button, click a polygon in the map or draw a box that intersects one or more polygons to select those features.
A selected polygon is highlighted in the map
Alternately, you can select polygons using attributes of polygon features.
To select polygons by attributes:
1. In the Legend, make sure the desired map layer is visible by placing a check in the box next to the layer’s name.
2. On the Search tab, click the Select by Attribute button.
3. In the dialog that opens, choose the layer of interest, an attribute of that layer, and then the value of the attribute that will be used to identify the polygon of interest. To choose the value, you can either select it from the list or type in the desired value.
4. With the attribute value highlighted, click OK to close the dialog and select the feature.
Choosing Keywords
To faciliate searching across a variety of data sources, each with their own naming conventions for hydrologic parameters, CUAHSI maintains an ontology of hydrologic keywords to which a given data source’s parameters are mapped. This means a search for the keyword Precipitation will return results even if a data source calls that parameter “rainfall” or “precip” instead.
You can choose from one or more of these keywords when conducting a search.
To quickly choose a single keyword:
1. In the Keyword panel on the Search tab, locate the drop down box where you can type a keyword.
2. Start typing the keyword, e.g., streamflow, in the box. The box autocompletes to a valid keyword based on what you type. Or, you can click the drop down arrow to choose a keyword from the list.
To select multiple keywords:
1. In the Search tab, click the Add More Keywords button.
2. In the dialog that opens, choose a keyword by either typing it in the text box at the top or by browsing the keywords and selecting a desired keyword.
3. With a keyword highlighted, click the green plus sign to add it to the list of selected keywords.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 to add more keywords.
5. Click OK when all desired keywords have been added.
Note: If you are interested in all variables, then select the top-level Hydrosphere keyword.
Setting a Time Range
Search results will only be returned if the period of record for a time series intersects the time range that you specify.
To quickly set the time range, enter the start and end dates into the boxes in the Time Range panel of the Search tab. Default values are provided as a guide.
For more advanced options regarding time ranges, click the Select Time button. This button opens a dialog in which you can manually set the start and end dates or quickly select a recent period such as the last month.
Choosing Data Sources
Dozens of data sources publish data using WaterOneFlow, making them accessible in HydroDesktop. These data sources register with CUAHSI’s HIS Central, where a catalog of all data sources and what parameters those data sources publish is maintained.
By default, when HydroDesktop performs a search, it sends the request to HIS Central. HIS Central searches its catalog to see what sites exist that match the search criteria, and search results are returned to HydroDesktop.
In many cases, this default behavior is fine and there is no need to modify this aspect of search. However, you do have a couple of advanced options available to you.
One of these options is to restrict the search to specific data sources. You might do this when you know you only want to work with USGS data.
To restrict the option to particular data sources:
1. On the Search tab, click the Select Data Sources button.
2. In the dialog that opens, place a check next to services that you want to include for the search, and click OK.
Another option you have is to search the local metadata cache instead of HIS Central. The metadata cache is a database, much like the one at HIS Central, which catalogs what parameters are available from certain data sources. However, the metadata cache is created by you and managed by you. It has no ties to HIS Central. Creating a metadata cache is useful if you are aware of services that are not registered at HIS Central. These services wouldn’t be returned in HIS Central search results, but may still be useful to you. For more information on creating a metadata cache, see Metadata Fetcher.
To search the metadata cache instead of HIS Central:
1. On the Search tab, click the Select Data Sources button.
2. In the dialog that opens, check the Local Data Source radio-button and click OK.
Note: You must have already harvested data into the metadata cache before attempting to search it.
Running a Search
With search parameters set, follow these steps to run a search:
1. In the Search tab, click the Run Search button.
2. When the dialog indicates the search has finished, click to Hide the dialog.
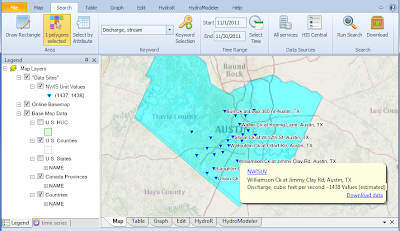
Locations of time series that match your search criteria are displayed in the map and symbolized by data source and number of data values available. You can hover your mouse over one of the symbols in the map to see more about that location.
Downloading Data
There are a couple of ways to download data from search results. The easiest is to hover the mouse over the location of a desired time series in the map, and in the pop-up window that opens, click the Download button.
If you would like to download multiple time series, then you can select them and click the Download button on the Search tab. You select series the same way you select other features in the map. For example, you can use the Select tool on the Map tab to click on or draw a box around the time series you want to download.
When the download begins, the Download Manager shows detailed progress of each download.
When the download completes, click to Hide the dialog. If any errors occur during the download, you can click to view the details of the download attempt or attempt to re-download the series with errors. You can also copy the error log so that you can post it to the HydroDesktop issue tracker, thereby alerting the development team to potential issues with the system.
With the download complete, you can now visualize, analyze, and export the data using HydroDesktop’s other capabilities.
The Metadata Fetcher
HIS Central maintains a catalog of time series metadata, i.e., where time series variables are measured and from which Web services they may be obtained. HydroDesktop queries HIS Central’s catalog when searching for data. But what happens when a service isn’t registered with HIS Central? This may happen when a service is developmental or if the service is private. HydroDesktop can still search for data from such services, but instead of searching HIS Central, the search is performed on a local metadata cache database.
The local metadata cache database is similar to the HIS Central catalog. Like the HIS Central catalog, the local metadata cache database doesn’t store time series values; it stores information about where time series variables are measured and from which Web services they may be obtained. One difference is that the variables in the local metadata cache database are not mapped to the CUAHSI hydrologic variable ontolgoy, because the ontology and mappings are maintained by HIS Central. Another difference is that the local metadata cache database only stores metadata from the services that you choose to harvest into it.
The Metadata Fetcher is the tool that you use to harvest metadata into the local metadata cache database. You’ll find it under the Data Sources Metadata panel added to the Search tab. The panel has buttons for working with the metadata cache.
The general workflow for harvesting metadata into your local cache is:
- Use the Add Data Source button to add WaterOneFlow services to the list of services that the metadata cache will harvest. This just adds services to a list and doesn’t actually perform any harvesting.
- Use the Manage button to harvest metadata for selected services.
- Once metadata has been harvested, you can search the local metadata cache database by using the Search tab. For more information on search see Searching for Data.
Managing Services
When you click the Manage button, the Metadata Fetcher window opens showing a list of WaterOneFlow Web services that can be harvested. The title of the service, its URL, and a timestamp indicating when the service was last harvested are displayed.
Note: If you see a timestamp for the year 0001, this indicates that metadata has not yet been harvested for the given service.
To update the local metadata cache database, place a check next to the service(s) that you want to harvest and click Download Metadata. The database will be updated with the latest metadata available from the service. Remember that you are not downloading time series values here. You are simply downloading metadata about where time series are measured to enable efficient searching for data later on.
In the Service Management menu, you’ll find options for adding services and removing checked services from the local metadata cache database. You can also refresh the service list if you suspect that the list of services displayed in the Metadata Fetcher window is not current.
Adding Services
The Add WaterOneFlow Service Info window is used to add WaterOneFlow Web services to the list of services for which metadata can be harvested into the local metadata cache database. You can open the Add WaterOneFlow Service Info window either by clicking Add in the Metadata panel of the Table tab in HydroDesktop, or by accessing the Service Management menu in the Metadata Fetcher window.
In the Add WaterOneFlow Service Info window, you can add information for one service at a time or for multiple services. Before updating the local metadata cache database with information about the services you want to add, you can check for any identical services already in the database by clicking the Check Existing button. This helps to avoid duplicate entries in the database. Click Update Database to add information about the services to the database.
Adding a Single Service
To add information about a single WaterOneFlow Web service:
In the Add WaterOneFlow Service Info window, activate the Add Single Service tab.
Fill out the information for a single service.
Optionally, click to check if the service already exists in the database.
Click to update the database.
Adding Multiple Services
To add information about multiple WaterOneFlow Web services, you have three options:
In the Add WaterOneFlow Service Info window, activate the Add Multiple Services tab and complete the information for each service to add.
In the Import menu, choose From HydroServer and input the URL to a HydroServer’s Capabilities service.
In the Import menu, choose From File and input the path to a comma delimited file containing information about the services to add. The names of the columns in the file must match the names in the Add Multiple Services tab.
For any of the options above, the result is a list of services in the Add Multiple Services tab. Once the list is complete, you can optionally click to check if the service already exists in the database. Then, click to update the database.
Note: A HydroServer is a Web server hosting one or more WaterOneFlow services. HydroServers also publish a Capabilities service which enables clients to automatically determine what services the HydroServer has to offer.
Options
In the Add WaterOneFlow Service Info window, from the Options menu, you can choose whether or not each service in the list should be checked to see if it matches the WaterOneFlow service signature before adding the service to the database. Checking the service requires following the given URL to see if a Web service is present, and if so, whether or not it has the same methods as defined by WaterOneFlow. This checking requires additional processing time, but helps to insure that only operational WaterOneFlow services are added to the metadata cache database.
EPA Delineate Watershed Tool
The EPA Tools in HydroDesktop provide access to EPA’s WATERS Web and Database Services. Users can use these tools to get the watershed and the flowlines that are delineated from the specified point on the map. Both the watershed and flowlines are based on NHD (National Hydrography Dataset) system.
Contact information for EPA’s WATERS Web and Database Services can be found at the following URL: http://www.epa.gov/waters/comments.html
Delineating Your Watershed
Using the EPA Delineation tool to create a watershed shapefile makes it possible to search for hydrological data within particular watersheds. To do this:
1. Click the Delineate button in the EPA Delineation Panel in the Home Tab.
2. Specify the names of Watershed Point, Watershed and Streamline for the files that you want to save.
3. Click OK. You will find the cursor turns to a cross shape.
4. Click at one point that you want to use as the outlet on the map.
5. The Delineation tool is now starting to collect the coordinate information of the point you clicked and send it to the EPA Web Services to get responses.
6. Wait until you see the message “Drawing Features on the Map...”. The message box will close automatically after all procedures are complete.
7. You will find three shapefiles with the names you specified shown on the top of the map. They are temporarily saved in UsersApplication DataHydroDesktopDelineation folder in your system.
8. You can export the features as shapefiles to other locations by right clicking on the name and selecting Data –> Export Data.
9. You can also check the attributes of these shapefiles by right clicking on the name and selecting View Attributes, or directly click the Attribute button in the ribbon tab.
Now you have a pretty hydrological view of all the upstream of your particular point.
 |
| A search for sites in the Charles River watershed using the EPA Watershed Delineation Tool. |